What is heart failure?
Heart failure, also referred to as congestive heart failure, is a serious medical condition that occurs when your heart stops pumping blood as efficiently as it should. Blood returns back to the heart faster than it can be distributed. This leads to congestion, where blood and fluid back up in other parts of your body like your lungs and legs. Types of heart failure include:
- Left-sided heart failure – This is the most common type of heart failure. It occurs when the left heart chamber, or ventricle, weakens and is unable to pump oxygenated blood around your body. The blood can back up into the lungs as a result and lead to organ damage as well as right-sided heart failure.
- Right-sided heart failure – Usually caused by left-sided heart failure, the job of the right heart chamber is to deliver blood to your lungs. If the left heart chamber is not working effectively and there is already blood backed up, the right side has to work much harder and can fail as a result.
- Diastolic heart failure – When the heart muscle stiffens, usually as a result of another heart condition, it cannot easily fill up and deliver blood to the necessary organs. This is known as a diastolic dysfunction and can occur in either side of the heart.
- Systolic heart failure – If your heart is enlarged or weakened, it cannot pump enough blood around your body for it to work normally. Fluid can build up in your blood vessels and leak into other spaces causing swelling and breathlessness. This can occur on either side of the heart.
Symptoms and causes
Heart failure is usually caused by another condition such as coronary artery disease, cardiomyopathy, or types of arrhythmias where the heartbeat has an irregular pattern. It can also be brought about by conditions that have an increased risk of heart failure such as high blood pressure, obesity and diabetes. Symptoms are wide ranging and can vary by patient. They may include chest pain, swelling, shortness of breath, fatigue, palpitations, weight gain and persistent coughing.
How is it diagnosed?
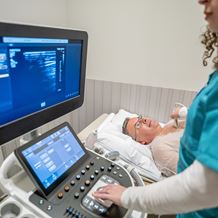
Your doctor will talk to you about your symptoms and medical history before referring you to a cardiologist for further examination. At your specialist appointment, your doctor will measure your pulse and blood pressure and test your heart function. This can be done using common testing devices all of which are designed to check the health of your heart:
Once heart failure has been diagnosed, it is categorised into four different stages of risk:
- Pre-heart failure – you may have a family history or medical condition.
- Pre-heart failure – part of your heart is not working well but you are not experiencing symptoms.
- Heart failure – you are experiencing symptoms.
- Advanced heart failure – this is the final stage.
How is it treated?
Heart failure can be treated as a chronic medical condition, and there are several highly effective medications available which can be increased over time to stabilise symptoms and dramatically improve outcomes. Your doctor may recommend particular devices and procedures to manage each stage of heart failure such as coronary angioplasty, implantable devices, pacemakers, and coronary bypass surgery (CABG). Regular long-term follow up is essential for patients, and cardiac rehabilitation and exercise are critical to managing the condition.

Other conditions
What's next?
If you have been experiencing heart-related symptoms, book an appointment with our cardiac services specialist today.
Our specialists in Cardiac Services
View all specialists